Professor Xu Kecheng summarizes the eight major roles of hydrogen in cancer control!
The effect of hydrogen on cancer was studied as early as 1975, when high-pressure hydrogen was used, which did not attract the attention of the medical community until
Japanese scholars discovered the biological effect of hydrogen in 2007: neutralizing toxic free radicals. In 2018, Professor Xu Kecheng achieved remarkable results by
using hydrogen absorbers as adjuvant therapy for tumors.
1. The role of hydrogen molecules in cancer: relieving cancer-related fatigue
Everyone will experience fatigue, but cancer patients are more prone to fatigue. Cancer fatigue is different from ordinary fatigue. Even if you sleep well, you still feel tired. No
matter how determined you are to stay alert, it is difficult to resist that lingering fatigue. The impact of fatigue on the quality of life of cancer patients exceeds the sum of nausea,
depression, and pain. Traditional measures for improving cancer-related fatigue may not be effective or have multiple adverse reactions, making it difficult for patients to tolerate.
Are there any measures that can produce results and be widely applied without side effects?
Perhaps hydrogen therapy meets the above requirements.
2. Hydrogen molecules can inhibit oxidative free radicals within antibodies
It is currently recognized that the accumulation of peroxide free radicals, also known as reactive oxygen species, is the central factor causing fatigue. This is a remarkable research
result in recent years.
Hydrogen molecules (H2) have the following functions in response to peroxide free radicals:
(1) Directly reducing hydroxyl radicals.
(2) Directly reducing peroxynitrite and regulating gene expression. Hydrogen molecules can scavenge another strong free radical, ONOO -.
(3) Regulating gene expression indirectly reduces oxidative stress. Hydrogen can improve peroxidation damage in an Nrf2 dependent manner.
3. Hydrogen molecules can eliminate inflammation
Inflammatory pathway activation is considered to be the basis for sustained fatigue in cancer patients is that fatigue usually begins during cancer treatment, and
chemotherapy and surgery can induce inflammatory responses.
In patients who actively receive treatment, an increase in inflammatory markers is associated with an increase in fatigue levels. In cancer survivors, despite discontinuing
cancer treatment, elevated levels of inflammatory markers were observed and correlated with fatigue levels.
Hydrogen molecules can reduce the expression of biological factors that promote inflammation and exert anti-inflammatory effects. There are many pro-inflammatory factors,
including NF - κ B, TNF - α, interleukin-1 β, IL-6, IL-10, IL-12, CCL2, interferon (INF) - γ, ICAM-1, PGE2, and PGE2. Korean scholars studied the effect of hydrogen rich water
on a chronic fatigue mouse model and found that compared with the control group treated with oral pure water, the inflammatory factors, serum TNF - α, IL-6, IL-17, and hepatic
IL-1 β in the hydrogen group were significantly reduced.
Inflammation can be infectious inflammation caused by infection or non infectious inflammation caused by non infection. Usually, acute inflammation is beneficial as it is the
body's automatic defense response, but chronic inflammation is often harmful and can cause many chronic diseases, especially cancer.
Cancer cells are traitors formed by genetic mutations during the replication process of normal cells under the influence of their own genetic defects or microenvironment. The number
of cancer cells produced is equal to the number of cell divisions multiplied by the number of mutated genes produced during each division. Due to inflammation, organ cell damage
will increase, cell division frequency will increase, and cell mutations will also increase, leading to an increase in cancer cell formation. Controlling inflammation can help control cancer.
In the study of brain injury models, it was found that hydrogen can reduce the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines; Using an animal model of systemic inflammatory response induced by yeast polysaccharides, it was found that inhaling hydrogen can reduce multi organ damage and improve mouse survival rate. This effect is mainly due to its reduction of
serum oxidative damage products, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF - α) production, and decrease in pro-inflammatory cytokine HMGB1 levels;
Cell and animal experiments have confirmed that hydrogen can inhibit the phosphorylation of extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK), reduce the expression of factors such as
N-terminal kinase (JNK), and prevent the translocation of phosphorylated ERK from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, thereby reducing the expression of inflammatory mediators and alleviating inflammatory responses;
In the study of ischemia-reperfusion kidney injury, it has also been found that hydrogen can reverse the expression of many inflammation related factors after reperfusion injury, thereby exerting a renal protective effect.
Regardless of the mechanism, it seems that hydrogen can exert anti-inflammatory effects, reduce the release of inflammatory factors, and inhibit tumor occurrence, progression, and metastasis. Of course, this requires further experimental research to confirm.
4. Hydrogen molecules have neuroprotective effects and improve sleep
Cancer patients often experience disrupted circadian rhythms and sleep disorders before, during, and after treatment. This abnormality is also a factor leading to
cancer-related fatigue.
Hydrogen molecules can improve sleep not only by eliminating chronic low-grade inflammation, but also due to their direct neuroprotective effects. There is a special
connection between the stomach and the brain, known as the stomach brain axis. Inhaled hydrogen gas activates the expression of beta adrenergic receptors, induces the
release of plasma ghrelin from the stomach, activates growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR) in the brain, promotes auxin production, exerts neuroprotective effects,
thereby maintaining normal circadian rhythms and improving sleep.
5. The effect of hydrogen absorption on cancer: inhibiting cancer cells
Hydrogen molecules can inhibit cancer cells, generally believed to be due to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. The most powerful and toxic oxidants in
the body are • OH and ONOO -, which can act on nucleic acids, lipids, and proteins, causing DNA damage, lipid peroxidation, and protein denaturation. Smoking, air
pollution, chemicals, mental stress, inflammation, etc. induce these peroxides, promote cell mutations, and trigger cancer cell formation. Hydrogen is a specific scavenger
for these two oxidants.

The concept of hydrogen selective antioxidant is to neutralize only these toxic reactive oxygen species, without affecting reactive oxygen species such as oxygen, nitric oxide,
and hydrogen peroxide that have an effect on the body.
Some people in Japan say that hydrogen is effective for 67 diseases; A scholar from the United States has published an article stating that hydrogen molecules can improve at
least 170 health conditions and diseases; Another American expert said that among the top ten causes of death in the United States, besides suicide and traffic accidents,
hydrogen can be improved.
6. The effect of hydrogen absorption on cancer: lung protection
Hydrogen can "protect" the lungs and has the effect of improving and preventing lung injury. The characteristics of hydrogen for lung protection include:
Firstly, hydrogen has strong diffusion ability.
Hydrogen has a small molecular weight and can easily penetrate biological membranes, entering the cytoplasm, mitochondria, and nucleus. The lungs are the organs closest to
the external environment, and hydrogen gas is more likely to enter the lungs;
Secondly, hydrogen has a selective antioxidant effect.
Hydrogen molecules can selectively react with free radicals hydroxide and peroxynitrite without reducing other reactive oxygen species related to cellular signaling (such as H2O2),
thus not affecting normal metabolic redox reactions in the body, nor does it affect the gas exchange of the lungs themselves;
Thirdly, hydrogen has strong biocompatibility.
The tissue compatibility of hydrogen molecules is higher than that of other antioxidants, which is particularly important for delicate tissues like the lungs and will not harm lung tissue;
Fourthly, hydrogen is particularly safe
Fifth, the lungs have abundant blood flow.
Whether inhaled or injected with a solution containing hydrogen, hydrogen can quickly penetrate through lung tissue and enter the whole body, which is extremely helpful for
improving the overall condition of the body;
Sixth, high hydrogen concentration may have a stronger effect.
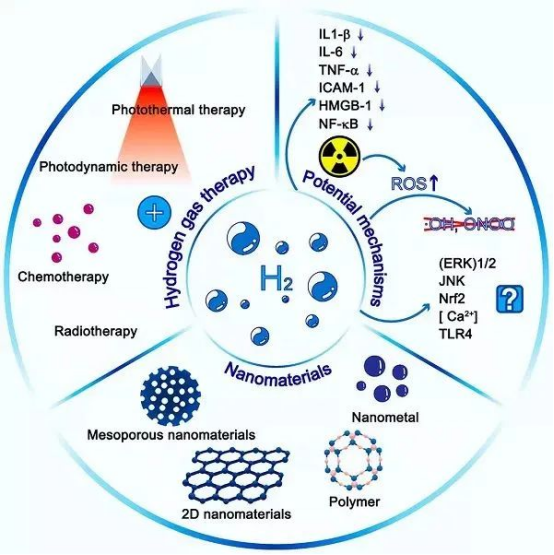
7. The role of hydrogen absorption in cancer: modifying cancer cells and microenvironment
Research has shown that hydrogen molecules can inhibit cancer cell proliferation and movement, promote cancer cell degeneration and apoptosis. Animals with axillary
tumors were given hydrogen (H2) or nitrogen (N2) gas for 6 hours a day, and the tumor formation was observed weekly. It was found that the hydrogen absorbing animals
had slow tumor formation and smaller tumors, indicating that hydrogen gas inhibited tumor growth.
Researchers further conducted cell culture experiments to compare the growth status of cancer cells under normal gas and hydrogen containing gas conditions. They found
that under hydrogen containing conditions, cancer cell proliferation slowed down, movement slowed down, degeneration and apoptosis occurred.
In 1975, American scholars Dole et al. published an article in the journal Science, reporting that administering 97.5% hydrogen to animals for continuous respiration at 8
atmospheres effectively inhibited skin squamous cell carcinoma. They first proposed that molecular hydrogen inhibits tumor growth through antioxidant activity.
Japanese scholars have found that drinking hydrogen water to animals with liver cirrhosis can prevent the occurrence of liver cancer. Treatment of tongue cancer cells with
hydrogen water resulted in inhibition of cancer cell growth.
Scholars from Shanghai Jiao Tong University have discovered that hydrogen can inhibit animal colon cancer by regulating the redox microenvironment, interfering with the
expression of genes related to cancer cell proliferation, thereby promoting cancer cell apoptosis and inhibiting cancer cell proliferation.
Hydrogen molecules have been proven to be a selective, non-toxic, residue free, and extremely inexpensive antioxidant substance. In the "elimination" and "transformation"
of Chinese style cancer control, hydrogen molecules seem to play a role in transforming cancer cells and the microenvironment.
8. The effect of hydrogen absorption on cancer: enhancing the efficacy of radiotherapy and chemotherapy, reducing the side effects of
radiotherapy and chemotherapy
In practice, hydrogen has at least two effects on cancer:
Firstly, hydrogen can "transform" cancer cells, making them more "compliant" and enhancing the effectiveness of radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
Secondly, hydrogen can reduce the side effects of radiotherapy and chemotherapy
Learn more: https://www.phyflow.com/about-us